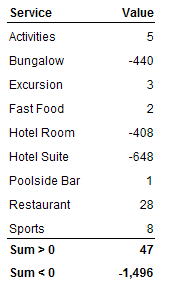
=Sum((If [Value]>0 Then [Value]) ForEach([Service]))
=Sum((If [Value]<0 Then [Value]) ForEach([Service]))
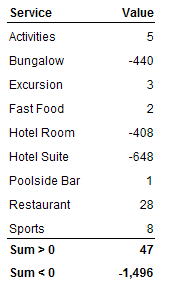
=Sum((If [Value]>0 Then [Value]) ForEach([Service]))
=Sum((If [Value]<0 Then [Value]) ForEach([Service]))
SP3 FP5.3
Create a report that contains 3 objects: Country, Year, Revenue

Add table with expression
=Sum(If([Year] Between (“FY2004″;”FY2006”); [Revenue]; 0))
Add section by Country
Everything looks nice

Now add new query with only Year.
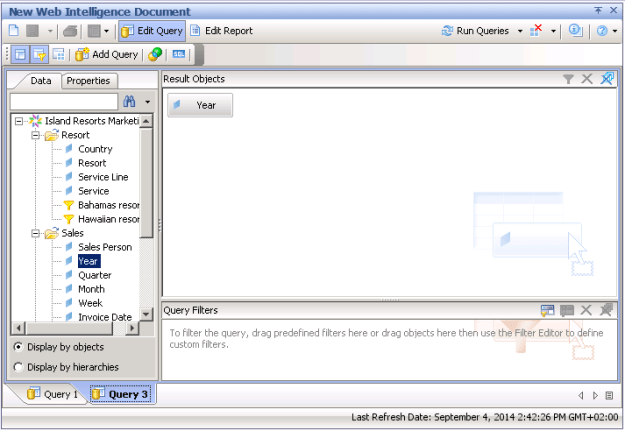
Now the expression produces null result. But why???
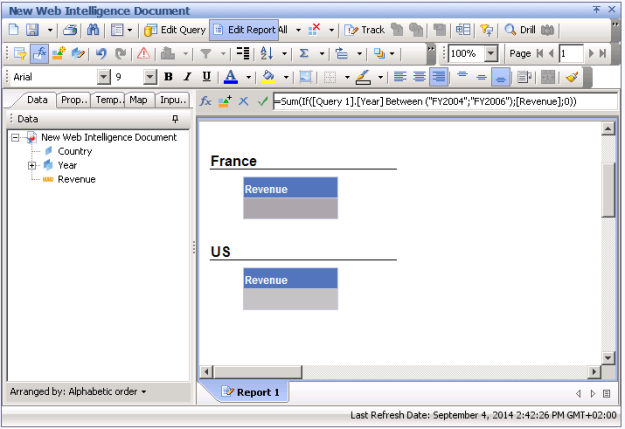
To see the numbers again, you can either unmerge Year (which is usually not an option)

or enable Extend merged dimension values
It is still not clear why this helps.
Two expressions
=[Revenue] Where ([Country]=”US”)
and
=Sum(If [Country]=”US” Then [Revenue])
might look similar. They produce the same result if Country is not used in the table:
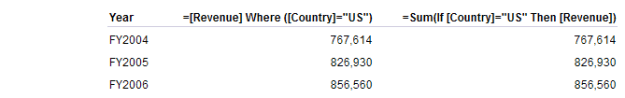
However with Country the result is slightly different

The expression with Where removes Country from the context, i.e. something like
=Sum(If [Country]=”US” Then [Revenue]) ForAll([Country])
Here are some simple templates for OpenDocument links
http://localhost:8080/OpenDocument/opendoc/openDocument.jsp?sType=wid&iDocID=00000
http://localhost:8080/OpenDocument/opendoc/openDocument.jsp?sType=wid&sIDType=CUID&iDocID=AAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
http://localhost:8080/OpenDocument/opendoc/openDocument.jsp?sType=wid&sPath=[Folder],[Subfolder]&sDocName=Document
http://localhost:8080/OpenDocument/opendoc/openDocument.jsp?sType=wid&sIDType=CUID&iDocID=AAAAAAAAAAAAAAA&sInstance=Last
=”<a target=’_blank’ href='”
+”../../opendoc/openDocument.jsp?sType=wid&sDocName=” + URLEncode(“Document“)
+”&lsSPrompt:=”+UserResponse(“Prompt:”)
+”‘>”+Text
+”</a>”
Here is some code for paged querying InfoStore (BO XI 3.1):
String uri = "path://InfoObjects/**[si_kind='Webi' and si_instance=0]"; PagingQueryOptions options = new PagingQueryOptions(); IPageResult ips = infoStore.getPagingQuery(uri, options); Iterator<String> pageResultIter = ips.iterator(); while (pageResultIter.hasNext()) { String pageQuery = pageResultIter.next(); IStatelessPageInfo pageInfo = infoStore.getStatelessPageInfo(pageQuery, options); String sql = pageInfo.getPageSQL(); System.out.println(sql); IInfoObjects infoobjects = infoStore.query(sql); // do something with the infoobjects ... }
Let’s look at it line by line.
String uri = "path://InfoObjects/**[si_kind='Webi' and si_instance=0]";
We will query all Webi documents in the CMS using path query. Double asterisk mean recursive search. Root Folder is displayed as Public Folders in InfoView.
PagingQueryOptions options = new PagingQueryOptions();
PagingQueryOptions determines how the result will be paged. You can provide some parameters to the constructor.
Details can be found in the documentationPagingQueryOptions.
IPageResult ips = infoStore.getPagingQuery(uri, options); Iterator<String> pageResultIter = ips.iterator();
Initial paging query provides string iterator. The iterator will return the same URI query but with paging parameters.
while (pageResultIter.hasNext()) {
String pageQuery = pageResultIter.next();
...
}
This is the classic way to loop using a Java iterator.
IStatelessPageInfo pageInfo = infoStore.getStatelessPageInfo(pageQuery, options); String sql = pageInfo.getPageSQL(); IInfoObjects infoobjects = infoStore.query(sql);
These lines builds the SQL queries to retrieve the objects of the page.
To export Webi report to MHTML, the function HTMLView.getContent(Writer,String,String) should be used.
// widoc is an instance of DocumentInstance Reports reports = widoc.getReports(); HTMLView htmlView = (HTMLView) reports.getItem(0).getView(OutputFormatType.MHTML); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("report.mhtml"); htmlView.getContent(fw,"",""); fw.close();
Make sure that libraries xpp3.jar, xpp3_min.jar, xalan.jar and xercesImpl.jar from common\4.0\java\lib\external are included in the class path.
Starting from BusinessObjects XI SP5, SAP Sybase SQL Anywhere is used as default database for BusinessObjects system databases (CMS and Audit). This post describes basics how to connect to the system databases using iSQL.
Starting from BusinessObjects XI SP5, SAP Sybase SQL Anywhere is used as default database for BusinessObjects system databases (CMS and Audit). This post describes steps how to add a new database and provides some information about SQLAnywhere tools.
There is an alternative to InfoStore sql query – it is BO URI queries. In some situations URI queries are significantly shorter and clearer.
For instance, if we need to find all Webi document in folder Test, we will have to run multiple queries to get the result with SQL queries. First you need to find Test folder in the root folder. Then you can only form a SQL to find Webi reports.
String sql0 = "select si_id from ci_infoobjects where si_parent_cuid='" + CeSecurityCUID.RootFolder.FOLDERS + "' and si_name='Test'"; int id = ((IInfoObject)infoStore.query(sql0).get(0)).getID(); String sql = "select si_id from ci_infoobjects where si_parentid=" + id + " and si_instance=0 and si_kind='Webi'";
Using URI queries, the logic is far clearer
String uri = "path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test/[si_kind='Webi' and si_instance=0]";
String sql = infoStore.getStatelessPageInfo(uri, new PagingQueryOptions()).getPageSQL();
(Both versions lack error handling)
I will try to describe syntax of URI. Non-terminal elements are marked in red.
protocol://expression[[condition]][@attributes][?parameters]
protocol = query | path | cuid | search
Condition should be a valid WHERE condition, attributes are fields separated by comma, parameters are speparated by ampersand and have format name=value. Conditions, attributes and parameters are optional
It is better to see it on an example.
path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test/**[si_kind=’Webi’ and si_instance=0]@si_name,si_description?OrderBy=si_parentid
here,
This query will find all Webi documents in folder Test (located in Public Folders) and its subfolders. The corresponding SQL query is
SELECT TOP 200 si_name,si_description,SI_CUID,SI_PARENT_CUID FROM CI_INFOOBJECTS WHERE SI_ANCESTOR IN (1851) AND (si_kind='Webi' and si_instance=0) ORDER BY si_parentid,SI_ID
(Here 1851 is the ID of Test folder).
The conditions are simply added to the where clause. Attributes are used to restrict the list of fields in select clause (SI_CUID and SI_PARENT_CUID will always be added). If attributes are not specified all fields will be returned. Properties are primarily used for paging query. You can specify order with OrderBy.
path://root/path
root = InfoObjects | AppObjects | SystemObjects | *
path = path/node[/]
where node can be name of object, search pattern (e.g. *de* all objects that contain ‘de’ in their name) or recursive search wild char **. If the experssion ends with slash, children will be returned.
For instance, here are the queries to find object in the root folder with name ‘Test’
| URI | path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test |
| SQL | SELECT TOP 200 SI_CUID, SI_NAME, SI_PARENT_CUID, SI_DESCRIPTION, SI_CREATION_TIME, SI_KIND, SI_CHILDREN, SI_OWNER, SI_PATH, SI_CORPORATE_CATEGORIES_ID, SI_PERSONAL_CATEGORIES_ID, SI_FILES, SI_INSTANCE, SI_SCHEDULE_STATUS, SI_LAST_SUCCESSFUL_INSTANCE_ID, SI_KEYWORD FROM CI_INFOOBJECTS WHERE SI_PARENTID IN (23) AND SI_NAME=’Test’ ORDER BY SI_ID |
where 23 is ID of the root folder (aka Public Folders).
(In the following examples, I will only show WHERE clause.)
Trailing slash says to find direct children:
| URI | path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test/ |
| SQL | … WHERE SI_PARENTID IN (1851) … |
Plus sign allows to include the parent in the result:
| URI | path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test+/ |
| SQL | … WHERE (SI_PARENTID IN (1851) OR SI_ID IN (1851)) … |
You can use asterisk character to search using pattern:
| URI | path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test/*de* |
| SQL | … WHERE SI_PARENTID IN (1851) AND SI_NAME LIKE ‘%de%’ … |
You can use a recursive search using double asterisk. The following query will return all objects in Test and its subfolders. Note a nice field SI_ANCESTOR that allows recursive search in folders:
| URI | path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test/** |
| SQL | … WHERE SI_ANCESTOR IN (1851) … |
You can combine
| URI | path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test+/** |
| SQL | … WHERE (SI_ANCESTOR IN (1851) OR SI_ID IN (1851)) … |
cuid://<list>/path
list = cuids | ids
cuids = cuids,cuid
ids = ids,id
You can either list IDs or CUIDs but you cannot mix them in the same list. For instance,
cuid://<AfRWaT5_131NlLLf5bRMLKY,AcgOFGfhCzJEg.VjnPaidmI>
cuid://<12,11>
You can use the path expression. For instance, the following URI query will find all objects in the folder with ID=1851 that contain ‘de’ in them.
| URI | cuid://<1851>/*de* |
| SQL | … WHERE SI_PARENTID IN (1851) AND SI_NAME LIKE ‘%de%’ … |
query://{sql}
For instance,
| URI | query://{select * from ci_infoobjects where si_parentid=1851}?BPPSIZE=99999 |
| SQL | SELECT TOP 99999 * FROM ci_infoobjects WHERE si_parentid=1851 ORDER BY SI_ID |
search://{pattern}?options
Patern is either a single word or quoted words
search://{Revenue}
search://{‘US’ ‘France’ ‘Germany’}
Options are separated by ampersand and have form name=value. Possible options are SearchName, SearchKeywords, SearchDescription, CaseSensitive, MatchAllWords, FindWithoutWords, MatchExact, IncludeInstances.
| URI | search://{‘US Report’}?CaseSensitive=true&MatchAllWords=true |
| SQL | SELECT TOP 200 SI_CUID, SI_NAME, SI_PARENT_CUID, SI_DESCRIPTION, SI_CREATION_TIME, SI_KIND, SI_OWNER, SI_CORPORATE_CATEGORIES_ID, SI_PERSONAL_CATEGORIES_ID, SI_FILES, SI_INSTANCE, SI_SCHEDULE_STATUS, SI_LAST_SUCCESSFUL_INSTANCE_ID, SI_KEYWORD FROM CI_INFOOBJECTS WHERE (((SI_NAME LIKE ‘%[U][S][ ][R][e][p][o][r][t]%’) OR (SI_KEYWORD LIKE ‘%[U][S][ ][R][e][p][o][r][t]%’)) AND (SI_INSTANCE=0)) ORDER BY SI_ID |
import com.crystaldecisions.sdk.exception.SDKException; import com.crystaldecisions.sdk.framework.*; import com.crystaldecisions.sdk.occa.infostore.*; import com.crystaldecisions.sdk.uri.*; import com.crystaldecisions.sdk.exception.*; public class Program { public static void main(String[] args) { IEnterpriseSession enterpriseSession = null; try { System.out.println("Connecting..."); ISessionMgr sessionMgr = CrystalEnterprise.getSessionMgr(); enterpriseSession = sessionMgr.logon("Administrator", "", "localhost", "secEnterprise"); IInfoStore infoStore = (IInfoStore) enterpriseSession.getService("InfoStore"); PagingQueryOptions options = new PagingQueryOptions(); String uri = "path://InfoObjects/Root Folder/Test/[si_kind='Webi' and si_instance=0]"; IStatelessPageInfo pageInfo = infoStore.getStatelessPageInfo(uri, options); String sql = pageInfo.getPageSQL(); System.out.println(uri); System.out.println(sql); } catch (SDKException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (enterpriseSession != null) { enterpriseSession.logoff(); } } System.out.println("Finished!"); } }
This post describes the typical workflow required to create a new Webi document in BO XI 3.1. You can download the compete code here  . We will consider an example how to create a simple Webi document based on Island Resorts Marketing universe that will display resort service and revenue from that service for US.
. We will consider an example how to create a simple Webi document based on Island Resorts Marketing universe that will display resort service and revenue from that service for US.


The first steps are establishing connection with the CMS and initializing the report engine.
// Connect to CMS ISessionMgr sessionMgr = CrystalEnterprise.getSessionMgr(); IEnterpriseSession enterpriseSession = sessionMgr.logon(user, pass, host, auth); // Initialize Webi report engine ReportEngines reportEngines = (ReportEngines) enterpriseSession.getService("ReportEngines"); ReportEngineType type = ReportEngines.ReportEngineType.WI_REPORT_ENGINE; ReportEngine reportEngine = (ReportEngine) reportEngines.getService(type);
First, we perform CMS query to find the universe Island Resorts Marketing (which is one of the standard sample universes). (It is assumed that the universe exists).
IInfoStore infoStore = (IInfoStore) enterpriseSession.getService("InfoStore"); String unvQuery = "select * from CI_APPOBJECTS where SI_KIND = 'Universe'" + " and SI_NAME='Island Resorts Marketing'"; IInfoObjects infoObjects = (IInfoObjects) infoStore.query(unvQuery); IInfoObject infoObject = (IInfoObject)infoObjects.get(0);
Second, we actually create a new document.
DocumentInstance documentInstance = reportEngine.newDocument("UnivCUID="+infoObject.getCUID());
After this we initialize some helper variables. Data Provider and Query describe the same (query). Query is an interface to add objects and conditions, change properties such as maximum row retrieved etc. Data Provider is an interface primarily to run, purge the query etc. Data Source is equivalent to universe. If universe has multiple queries but each query use the same universe, there will be only one data source. Data Source provides all available objects in the universe.
DataProviders dps = documentInstance.getDataProviders(); DataProvider dataProvider = dps.getItem(0); Query query = dataProvider.getQuery(); DataSource dataSource = dataProvider.getDataSource();
First, we add a couple of objects available in the data source – Service and Revenue.
DataSourceObjects objects = dataSource.getClasses(); query.addResultObject(objects.getChildByName("Service")); query.addResultObject(objects.getChildByName("Revenue"));
Second, we construct the condition. The condition is County=’US’.
ConditionContainer container = query.createCondition(LogicalOperator.AND); ConditionObject conditionObject = container.createConditionObject(objects.getChildByName("Country")); FilterCondition filterCondition = conditionObject.createFilterCondition(Operator.EQUAL); filterCondition.createFilterConditionConstant("US");
The last step is to run queries.
dataProvider.runQuery();
So now we can add report to the document structure. Report container contains report header, body and footer.
ReportStructure reportStructure = documentInstance.getStructure();
ReportContainer reportContainer = reportStructure.createReport("My Report");
ReportBody reportBody = reportContainer.createReportBody();
In this example, we create a table with the two fields.
ReportBlock reportBlock = reportBody.createBlock(); ReportDictionary reportDictionary = documentInstance.getDictionary(); BlockAxis hAxis = reportBlock.getAxis(TableAxis.HORIZONTAL); hAxis.addExpr(reportDictionary.getChildByName("Service")); hAxis.addExpr(reportDictionary.getChildByName("Revenue"));
When the report is created from scratch, all default values are blanks and zeros so it is important to set the necessary attributes such as color, font, width.
SimpleTable simpleTable = (SimpleTable)reportBlock.getRepresentation(); CellMatrix bodyMatrix = simpleTable.getBody(); CellMatrix headerMatrix = simpleTable.getHeader(null); CellMatrix[] matrices = new CellMatrix[]{bodyMatrix, headerMatrix}; for (CellMatrix matrix : matrices) { for (int i=0; i<matrix.getColumnCount();++i) { TableCell cell = matrix.getCell(0, i); Attributes attributes = cell.getAttributes(); if (matrix == bodyMatrix) { attributes.setBackground(Color.white); attributes.setForeground(Color.black); } else { attributes.setBackground(new Color(81, 117,185)); attributes.setForeground(Color.white); } SimpleBorder border = (SimpleBorder)attributes.getBorder(); border.setSize(BorderSize.NONE); cell.setAttributes(attributes); Font font = cell.getFont(); font.setName("Arial"); font.setSize(10); cell.setFont(font); Alignment alignment = cell.getAlignment(); alignment.setHorizontal(HAlignmentType.LEFT); cell.setAlignment(alignment); cell.setWidth(50); } }
The final step is to apply format. It is important. If you miss this step, the report structure will not be modified.
documentInstance.applyFormat();
The final step is to save the document to a folder. We can use function
DocumentInstance.saveAs(title, int destinationFolderId, categories, personalCategories, overwrite)
First we need to find the destination folder id. We assume that the folder Report Samples exists.
String folderQuery = "select * from CI_INFOOBJECTS where SI_KIND = 'Folder'" + " and SI_NAME='Report Samples'"; infoObjects = (IInfoObjects) infoStore.query(folderQuery); infoObject = (IInfoObject)infoObjects.get(0); int folderId = infoObject.getID();
Now we can save the document with title “Test”.
documentInstance.saveAs("Test", folderId, null, null, true); documentInstance.closeDocument();
Hope this helps.